A. Indra Penglihatan (Mata)
Bagian-nagian bola mata beserta fungsinya sebagai berikut:
1. Sklera, melindungi bola mata dari kerusakan mekanis.
2. Kornea, menerima rangsangan cahaya.
3. Koroidea, menyediakan oksigen dan makanan bagi bagian mata yang lain.
4. Iris, melindungi refleksi cahaya dan mengendalikan kerja pupil.
5. Pupil, mengatur banyak sedikitnya cahaya yang diperlukan mata.
6. Lensa, membiaskan dan memfokuskan cahaya agar bayangan benda tepat jatuh di retina.
7. Aqueous Humor, merupakan cairan encer untuk menjaga bentuk kantong bola dalam mata.
8. Vitreous Humor, merupakan cairan bening dan kental untuk meneruskan rangsangan ke bagian dalam mata.
9. Retina, menerima bayangan dan untuk melihat benda.
10. Fovea sentralis, merupakan tempat bayangan jatuh pada retina.
11. Saraf mata, meneruskan rangsang cahaya ke saraf optik.
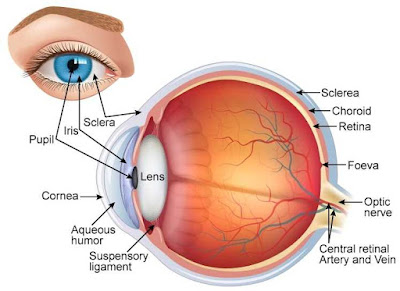
Bagian-bagian mata
B. Indra Pendengar (telinga)
Bagian-bagian telinga beserta fungsinya sebagai berikut:
1. Daun telinga, mengumpulkan dan gelombang bunyi.
2. Saluran telinga, mengkonsentralisasikan gelombang suara.
3. Membran timpani, menangkap getaran bunyi dan menyalurkannya ke tulang-tulang pendengar.
4. Tulang pendengar (malleus, incus, stapes), yaitu menghubungkan telinga luar dengan telinga dalam.
5. Rumah siput (koklea), terdapat reseptor pendengaran yang meneruskan rangsang getaran bunyi ke otak.
6. Organ korti, meneruskan rangsang getaran bunyi ke saraf auditori.
7. Tiga saluran setengah lingkaran, merupakan alat keseimbangan tubuh.

Bagian-bagian telinga
Cara kerja telinga secara mekanisme:
Getaran suara-> daun telinga-> saluran telinga-> membrane timpani -> malleus-> incus-> stapes-> Koklea-> organ korti-> sel saraf auditori-> otak.
C. Indra Perasa dan Peraba (kulit)
Susunan saraf indra peraba ada dua macam sebagai berikut:
1. Ujung saraf yang bebas yaitu indra peraba yang bertanggung jawab atas nyeri atau sakit.
2. Ujung saraf yang berselaput yaitu badan Paccini yang peka terhadap rangsang tekanan, badan Ruffini yang peka terhadap rangsang panas, badan Crausse yang peka terhadap rangsang dingin , seta badan Meissner yang peka terhadap rangsang sentuhan.

bagian-bagian kulit
D. Indra Pengecap (lidah)
Fungsi- fungsinya:
1. Ujung lidah, mengecap rasa manis.
2. Pangkal lidah, mengecap rasa pahit.
3. Tepi lidah depan, mengecap rasa asin.

A. Vision Senses (Eye)
The parts of the eyeball and its functions as follows:
1. Sclera, protect eyes from mechanical damage.
2. Cornea receives light stimulus.
3. Koroidea, provide oxygen and food for another part of the eye.
4. Iris, protect reflection of light and controls the work of the pupil.
5. Pupils arranged more or less light is needed an eye.
6. Lens, refract and focus the light so that proper shadows fall on the retina.
7. Aqueous humor, a watery fluid to keep the ball in the form of eye bags.
8. Vitreous Humor is a clear liquid and viscous to pass stimulus into the interior of the eye.
9. Retina, receive images and to view the objects.
10. The fovea centralis is where the shadow falls on the retina.
11. Nerves eyes, forward light stimuli to the optic nerve.
 |
| Parts of the eye |
B. Listener Senses (Ear)
The parts of the ear and its functions as follows:
1. Earlobe, collecting and sound waves.
2. The Ear Canal, sound waves concentrate.
3. The Tympanic Membrane, the sound vibrations capture and distribute it to the bones of the listener.
4. Bone listeners (malleus, incus, stapes), which connects the outer ear to the inner ear.
5. The House Snail (cochlea), there are receptors that transmit excitatory hearing the sound vibrations to the brain.
6. Organ of Corti passes on sound vibrations to stimulate the auditory nerve.
7. Three semicircular canals, the tool body balance.
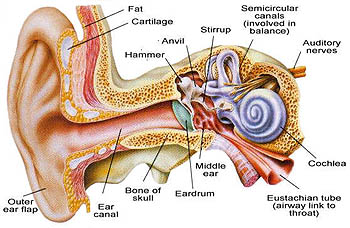
The workings of the mechanism of the ear:
Vibration voice> earlobe> ear canal> tympanic membrane -> malleus-> incus-> stapes-> Koklea-> korti- organ> nerve cells auditori-> brain.
C. Taste and Touch Senses (skin)
Nervous system there are two kinds of sense of touch as follows:
1. The free nerve endings that sense of touch which is responsible for pain or illness.
2. The nerve endings that are webbed body Paccini sensitive to stimuli of pressure, Ruffini bodies are sensitive to thermal stimuli, weight Crausse sensitive to cold stimuli, as well as the body Meissner-sensitive sense of touch.
parts of skin D. Taste buds (tongue).
It's functions:
1. The tip of the tongue savors the sweetness.
2. The base of the tongue, tasting the bitter taste.
3. The front edge of the tongue, tasting the saltiness.


0 Comments